Anterior Lens Luxation
Ophthalmology
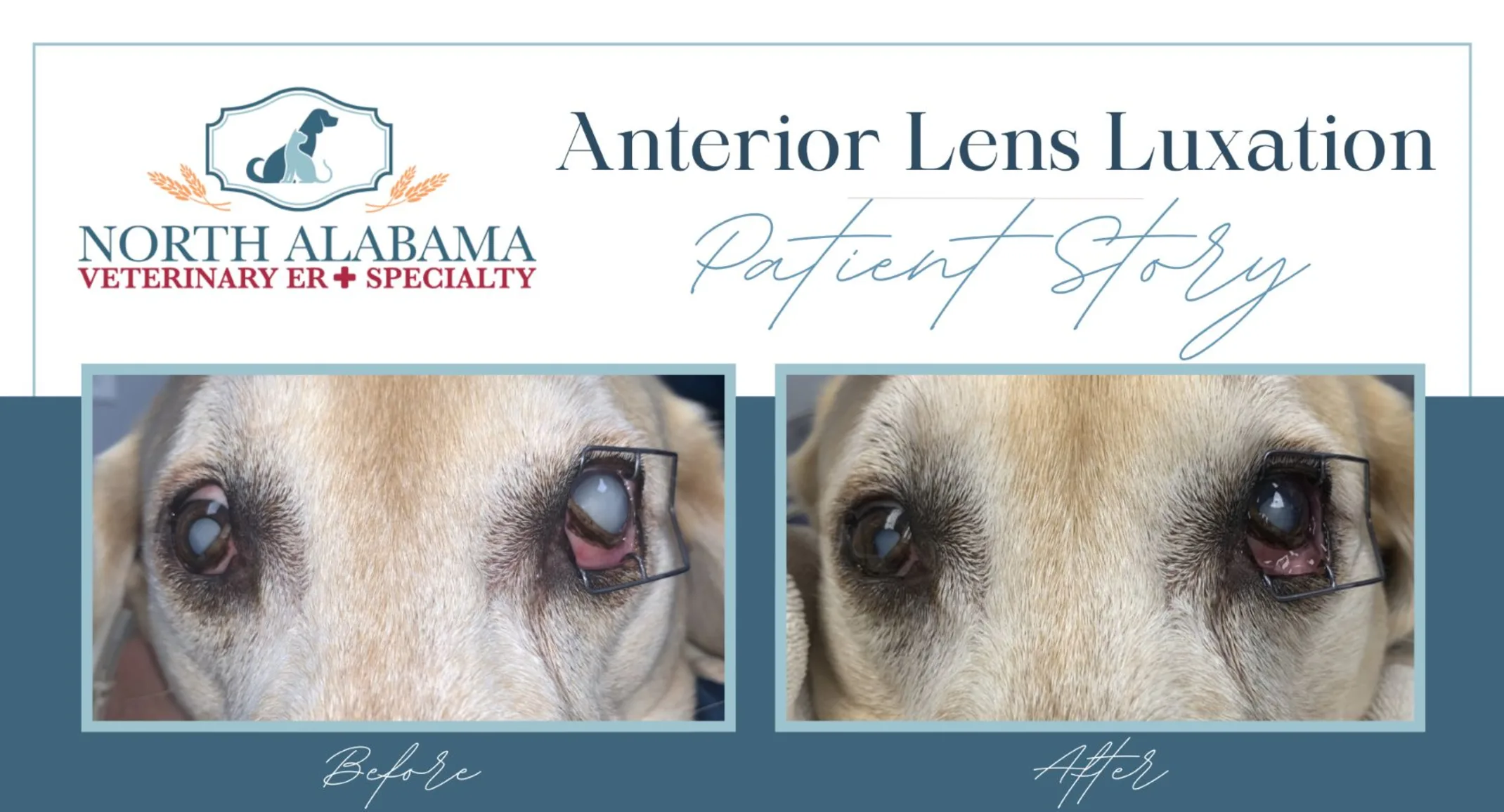
Jaxon presented to the Ophthalmology service on an emergency basis for acute squinting, tearing, and discomfort in his left eye. He was diagnosed with anterior lens luxation with secondary glaucoma. Anterior lens luxation occurs when the lens is displaced into the front part of the eye. This is an ocular emergency as it can block the outflow of fluid from the eye and lead to increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma).
A trans-corneal lens reduction was performed, which is a non-surgical procedure that displaces the lens from the front part of the eye into the back part of the eye. After this procedure, life-long topical therapy to keep the pupil constricted is needed to help keep the lens in the back part of the eye. The procedure was successful, the intraocular pressure returned to normal, and Jaxon was much more comfortable!
Pre: Before the procedure. The left eye has an eyelid speculum and shows the lens that is luxated anteriorly.
Post: After the procedure, the left lens is behind the iris.
